1. 简介#
单源最短路径问题是图论中的一个非常经典的问题,它的目标是在一个带权的有向图或无向图中,找到从一个指定的“源”顶点到图中所有其他顶点的最短路径(路径上所有边的权重之和最小)。这个问题在实际生活中有很多重要的应用,比如网络路由、地图导航、通信网络优化等。
主要的单源最短路径算法主要有以下三个:
- Dijkstra 算法:最著名和最常用的算法,但前提是图中所有边的权重都必须是非负的。
- Bellman-Ford 算法:比 Dijkstra 算法更具普适性,可以处理带有负权重边的图。同时,它还能检测图中是否存在“负权环”。
- SPFA 算法 (Shortest Path Faster Algorithm):这是 Bellman-Ford 算法的一种优化版本,在很多情况下(特别是稀疏图)比 Bellman-Ford 更快,同样可以处理负权边和检测负权环。
2. Dijkstra 算法#
Dijkstra 算法(迪杰斯特拉算法) 是一种贪心算法。它的核心思想是,每次都从“尚未确定最短路径”的顶点中,选择一个距离源点最近的顶点,并且认为这个顶点的最短路径已经确定,然后用这个顶点去更新其他相邻顶点的距离。
算法步骤如下:
- 初始化:
- 创建一个距离数组
dist,dist[i]表示从源点startNode到顶点i的当前最短距离。将dist[startNode]初始化为0,其他所有顶点的dist初始化为无穷大 (INF)。 - 创建一个优先队列
pq,并将{0, startNode}(表示距离为0,顶点为 startNode)加入队列。优先队列会根据距离从小到大排序。
- 创建一个距离数组
- 主循环:当优先队列不为空时,执行以下操作:
- 从优先队列中取出距离最小的顶点
u(以及其距离d)。 - 如果
d大于dist[u],说明已经有更短的路径到达u了(这个旧的、较长的路径信息是冗余的),直接跳过本次循环。 - 遍历
u的所有邻接点v(权重为w),进行松弛操作:如果通过u到达v的路径比已知的到v的最短路径还要短(即dist[u] + w < dist[v]),那么就更新dist[v]为dist[u] + w,并将新的、更短的路径信息{dist[v], v}加入优先队列。
- 从优先队列中取出距离最小的顶点
- 结束:循环结束后,dist 数组中就存储了从源点到所有其他顶点的最短路径长度。
C++ 代码实现如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <limits>
const int INF = std::numeric_limits<int>::max(); // 代表无穷大
struct Edge
{
int u, v, weight; // 边的起点、终点和权重
};
//{权重,顶点}
using ipair = std::pair<int, int>; // 用于存储权重和顶点的对
// Dijkstra 算法实现
// V: 顶点数量
// startNode: 源点
// Edge: 图的边列表{u, v, weight}
void dijkstra(int V, int startNode, std::vector<Edge> edges)
{
// 距离数组,初始化为无穷大
std::vector<int> dist(V, INF);
dist[startNode] = 0;
// 邻接表表示图
std::vector<std::vector<ipair>> adj(V);
for (const auto &edge : edges)
{
// 有向图
adj[edge.u].push_back({edge.weight, edge.v});
// 如果是无向图,则添加以下行
// adj[edge.v].push_back({edge.weight, edge.u});
}
// 优先队列(最小堆),存储 {距离, 顶点}
// std::greater 使其成为最小堆
std::priority_queue<ipair, std::vector<ipair>, std::greater<ipair>> pq;
pq.push({0, startNode});
while (!pq.empty())
{
// 取出当前已知最短路径的顶点
int u = pq.top().second;
int d = pq.top().first;
pq.pop();
// 如果这个顶点的最短路径已经被更新过,则跳过
if (d > dist[u])
{
continue;
}
// 遍历所有邻接点
for (auto &edge : adj[u])
{
int v = edge.second;
int weight = edge.first;
// 松弛操作
if (dist[u] + weight < dist[v])
{
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
pq.push({dist[v], v});
}
}
}
// 打印从源点到所有顶点的最短距离
std::cout << "Dijkstra 算法的结果:" << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
{
if (dist[i] == INF)
{
std::cout << "顶点 " << startNode << " -> " << i << ": No path" << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "顶点 " << startNode << " -> " << i << ": " << dist[i] << std::endl;
}
}
}
int main()
{
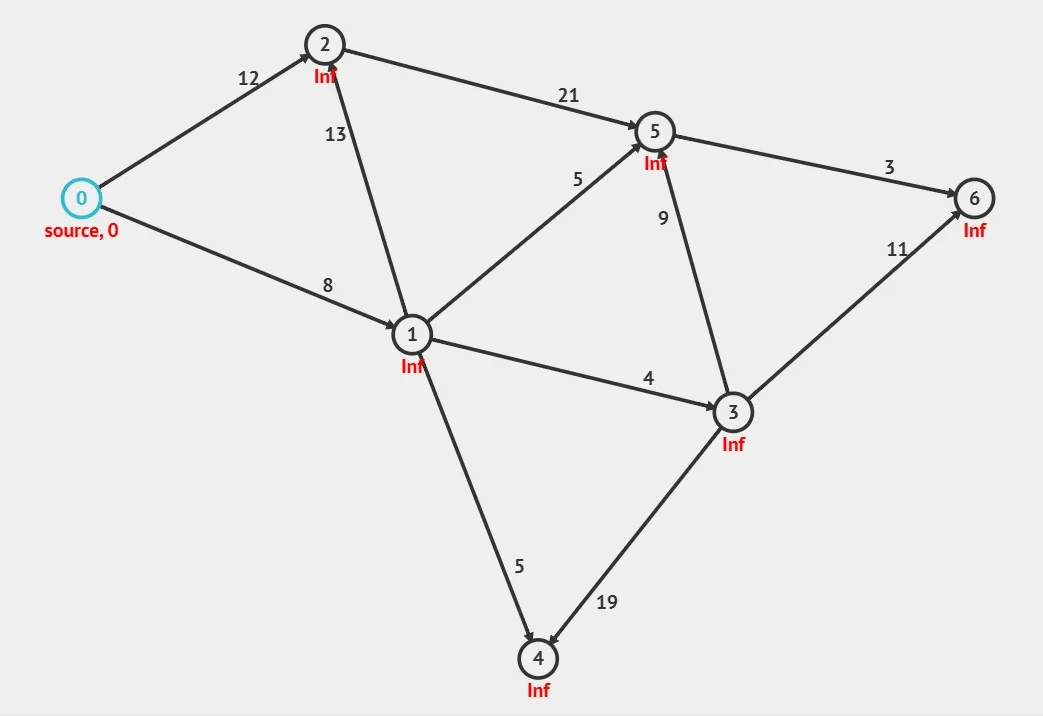
int V = 7; // 顶点数
int startNode = 0;
std::vector<Edge> edges =
{
{0, 1, 8},
{0, 2, 12},
{0, 3, 19},
{0, 4, 21},
{1, 2, 13},
{1, 3, 4},
{1, 4, 5},
{1, 5, 5},
{2, 5, 21},
{3, 4, 19},
{3, 6, 11},
{5, 3, 9},
{5, 6, 3}};
dijkstra(V, startNode, edges);
return 0;
}代码输出:
Dijkstra 算法的结果:
顶点 0 -> 0: 0
顶点 0 -> 1: 8
顶点 0 -> 2: 12
顶点 0 -> 3: 12
顶点 0 -> 4: 13
顶点 0 -> 5: 13
顶点 0 -> 6: 16动画演示过程如下:
3. Bellman-Ford 算法#
Bellman-Ford 算法(贝尔曼-福特算法) 同样用于解决单源最短路径问题,但它比 Dijkstra 更强大,因为它可以处理带负权边的图,并且能够检测负权环。
Bellman-Ford 的核心思想是动态规划。它通过对图中所有的边进行 V-1 轮松弛操作来逐步逼近最短路径。
- 经过第 1 轮松弛,可以找到从源点出发、最多经过 1 条边的最短路径。
- 经过第 2 轮松弛,可以找到从源点出发、最多经过 2 条边的最短路径。
- 经过
V-1轮松弛,可以找到从源点出发、最多经过V-1条边的最短路径。因为在一个不包含负权环的图中,任意两点间的最短路径最多包含V-1条边。
算法步骤如下:
- 初始化:
- 创建一个距离数组
dist,将源点startNode的距离dist[startNode]初始化为0,其他所有顶点的dist初始化为无穷大 (INF)。
- 创建一个距离数组
- 迭代松弛:
- 重复
V-1次以下操作: - 遍历图中的每一条边
(u, v),其权重为w。 - 松弛操作:如果
dist[u] + w < dist[v],则更新dist[v]为dist[u] + w。
- 重复
- 检测负权环:
- 完成
V-1轮松弛后,再进行第V轮松弛: - 遍历图中的每一条边
(u, v)。 - 如果仍然可以进行松弛操作(即
dist[u] + w < dist[v]),则说明图中存在一个从源点可达的负权环。因为在没有负权环的情况下,V-1轮后所有最短路径都已确定,不应再有更新。
- 完成
C++ 代码实现如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <limits>
const int INF = std::numeric_limits<int>::max(); // 代表无穷大
struct Edge
{
int u, v, w; // 边的起点、终点和权重
};
// Bellman-Ford 算法实现
// V: 顶点数量, E: 边的数量
// edges: 边的列表
// startNode: 源点
void bellmanFord(int V, int startNode, const std::vector<Edge> &edges)
{
std::vector<int> dist(V, INF);
dist[startNode] = 0;
// 1. 进行 V-1 轮松弛操作
for (int i = 0; i < V - 1; ++i)
{
for (const auto &edge : edges)
{
if (dist[edge.u] != INF && dist[edge.u] + edge.w < dist[edge.v])
{
dist[edge.v] = dist[edge.u] + edge.w;
}
}
}
// 2. 检测负权环
bool hasNegativeCycle = false;
for (const auto &edge : edges)
{
if (dist[edge.u] != INF && dist[edge.u] + edge.w < dist[edge.v])
{
hasNegativeCycle = true;
break;
}
}
// 3. 打印结果
std::cout << "Bellman-Ford 算法的结果:" << std::endl;
if (hasNegativeCycle)
{
std::cout << "图中包含负权重环!" << std::endl;
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
{
if (dist[i] == INF)
{
std::cout << "顶点 " << startNode << " -> " << i << ": No path" << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "顶点 " << startNode << " -> " << i << ": " << dist[i] << std::endl;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int V = 6; // 顶点数
int startNode = 0;
std::vector<Edge> edges =
{
{0, 1, -5},
{0, 2, 2},
{1, 2, 3},
{1, 3, 4},
{1, 4, 5},
{2, 5, 1},
{3, 4, 2},
{3, 5, 2},
{4, 5, 3},
{5, 1, -2}};
bellmanFord(V, startNode, edges);
return 0;
}代码输出:
Bellman-Ford 算法的结果:
顶点 0 -> 0: 0
顶点 0 -> 1: -5
顶点 0 -> 2: -2
顶点 0 -> 3: -1
顶点 0 -> 4: 0
顶点 0 -> 5: -14. SPFA 算法#
SPFA 算法是 Bellman-Ford 算法的一种队列优化版本,同样用于解决单源最短路径问题,并且能够处理负权边和检测负权环。
Bellman-Ford 算法的瓶颈在于它每一轮迭代都会盲目地尝试松弛所有的边,而实际上,只有那些在上一轮中距离被缩短了的顶点,才有可能去更新它们的邻接点。而SPFA 算法正是基于这个观察进行优化。它维护一个队列,队列中存放的是“刚刚被成功松弛过”的顶点。算法每次从队列中取出一个顶点 u,然后用 u 去松弛它的所有邻接点 v。如果 v 被成功松弛,并且 v 当前不在队列中,就将 v 加入队列。这个过程不断重复,直到队列为空。
由于只有“可能引发更新”的顶点才会入队并被用于松弛操作,SPFA 在大多数情况下(尤其是稀疏图)避免了 Bellman-Ford 中的大量冗余计算,因此平均效率要高得多。
算法步骤如下:
- 初始化:
- 创建一个距离数组
dist,将源点startNode的距离dist[startNode]初始化为 0,其他所有顶点的dist初始化为无穷大 (INF)。 - 创建一个队列
q,并将源点startNode入队。 - 创建一个布尔数组
in_queue,用于标记顶点是否在队列中。将in_queue[startNode]设为 true。 - 创建一个计数器数组
count,count[i]记录顶点i入队的次数,用于检测负权环。
- 创建一个距离数组
- 主循环:当队列
q不为空时:- 从队首取出一个顶点
u,并将其出队。将in_queue[u]设为false。 - 遍历
u的所有邻接点v(权重为w):- 松弛操作:如果
dist[u] + w < dist[v],则更新dist[v]为dist[u] + w。 - 如果
v被成功松弛,且v当前不在队列中: - 将
v入队,并设置in_queue[v]为true。 - 增加
v的入队计数count[v]。 - 检测负权环:如果
count[v]大于等于图的顶点总数V,则说明从源点到v的路径上存在一个负权环。算法可以立即终止并报告。
- 松弛操作:如果
- 从队首取出一个顶点
- 结束:如果队列为空且没有检测到负权环,
dist数组就包含了源点到所有其他顶点的最短路径。
C++ 代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <limits>
const int INF = std::numeric_limits<int>::max(); // 代表无穷大
struct Edge
{
int to; // 边的终点
int weight; // 边的权重
};
// SPFA 算法实现
// V: 顶点数量
// adj: 邻接表表示的图
// startNode: 源点
void spfa(int V, int startNode, const std::vector<std::vector<Edge>> &adj)
{
std::vector<int> dist(V, INF);
std::vector<int> inQueueCount(V, 0); // 记录每个顶点入队的次数
std::vector<bool> inQueue(V, false); // 标记顶点是否在队列中
std::queue<int> q;
dist[startNode] = 0;
q.push(startNode);
inQueue[startNode] = true;
inQueueCount[startNode]++;
bool hasNegativeCycle = false;
while (!q.empty())
{
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
inQueue[u] = false;
for (const auto &edge : adj[u])
{
int v = edge.to;
int w = edge.weight;
if (dist[u] != INF && dist[u] + w < dist[v])
{
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
if (!inQueue[v])
{
q.push(v);
inQueue[v] = true;
inQueueCount[v]++;
// 如果一个顶点入队次数超过 V,则存在负权环
if (inQueueCount[v] > V)
{
hasNegativeCycle = true;
goto end_loop; // 跳出外层循环
}
}
}
}
}
end_loop:;
// 3. 打印结果
std::cout << "SPFA 算法的结果:" << std::endl;
if (hasNegativeCycle)
{
std::cout << "图中包含负权重环!" << std::endl;
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
{
if (dist[i] == INF)
{
std::cout << "顶点 " << startNode << " -> " << i << ": No path" << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "顶点 " << startNode << " -> " << i << ": " << dist[i] << std::endl;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int V = 6; // 顶点数
int startNode = 0;
// 为了使用 SPFA,最好将边列表转换为邻接表
std::vector<std::vector<Edge>> adj(V);
std::vector<std::pair<int, std::pair<int, int>>> edges =
{
{0, {1, -5}},
{0, {2, 2}},
{1, {2, 3}},
{1, {3, 4}},
{1, {4, 5}},
{2, {5, 1}},
{3, {4, 2}},
{3, {5, 2}},
{4, {5, 3}},
{5, {1, -2}}};
for (const auto &edge_info : edges)
{
int u = edge_info.first;
int v = edge_info.second.first;
int w = edge_info.second.second;
adj[u].push_back({v, w});
}
spfa(V, startNode, adj);
return 0;
}输出结果为:
SPFA 算法的结果:
顶点 0 -> 0: 0
顶点 0 -> 1: -5
顶点 0 -> 2: -2
顶点 0 -> 3: -1
顶点 0 -> 4: 0
顶点 0 -> 5: -1